Management of Acute Care Surgery Patients at High Risk for Severe Alcohol Withdrawal
exp date isn't null, but text field is
INCLUSION CRITERIA
- Patient is considered high risk if known prior history of withdrawal delirium tremens +/- seizures AND recent alcohol use prior to admission
- OR
- ≥ 2 of the following:
- Recent regular alcohol use for ≥ 2 weeks/alcohol dependence
- Active symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal
- EtOH ≥ 200 mg/dl
- Positive CAGE assessment (CAGE abuse screening tool)
INCLUSION CRITERIA
- If both the MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume) and AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase) are normal patient is unlikely to be at high risk for severe alcohol withdrawal, consider MAWS (Michigan Alcohol Withdrawal Severity)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Traumatic brain injury with acute intracranial abnormality or need for frequent serial neurologic assessments (every 1-2 hours)
- Anticipated discharge in less than 24 hours
- Caution in elderly patients, renal failure or tenuous respiratory or mental status.
CONSIDERATIONS
- Admit to ICU
- Obtain IV access
- Apply cardiac monitors, continuous pulse oximetry, end-tidal CO2 monitoring
- Consider alternative diagnoses/causes of altered mental status (i.e. hypoglycemia, intracranial pathology)
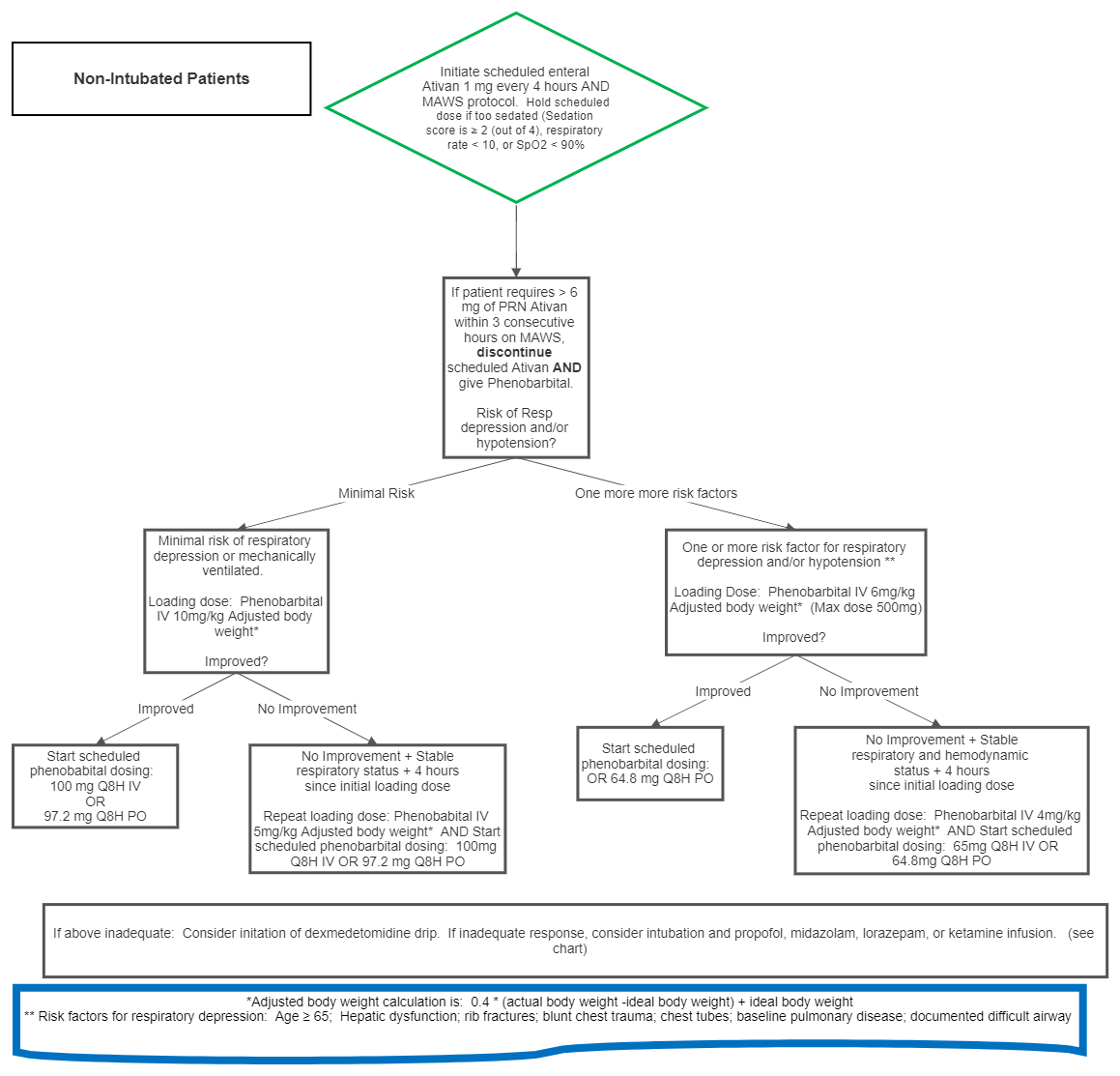
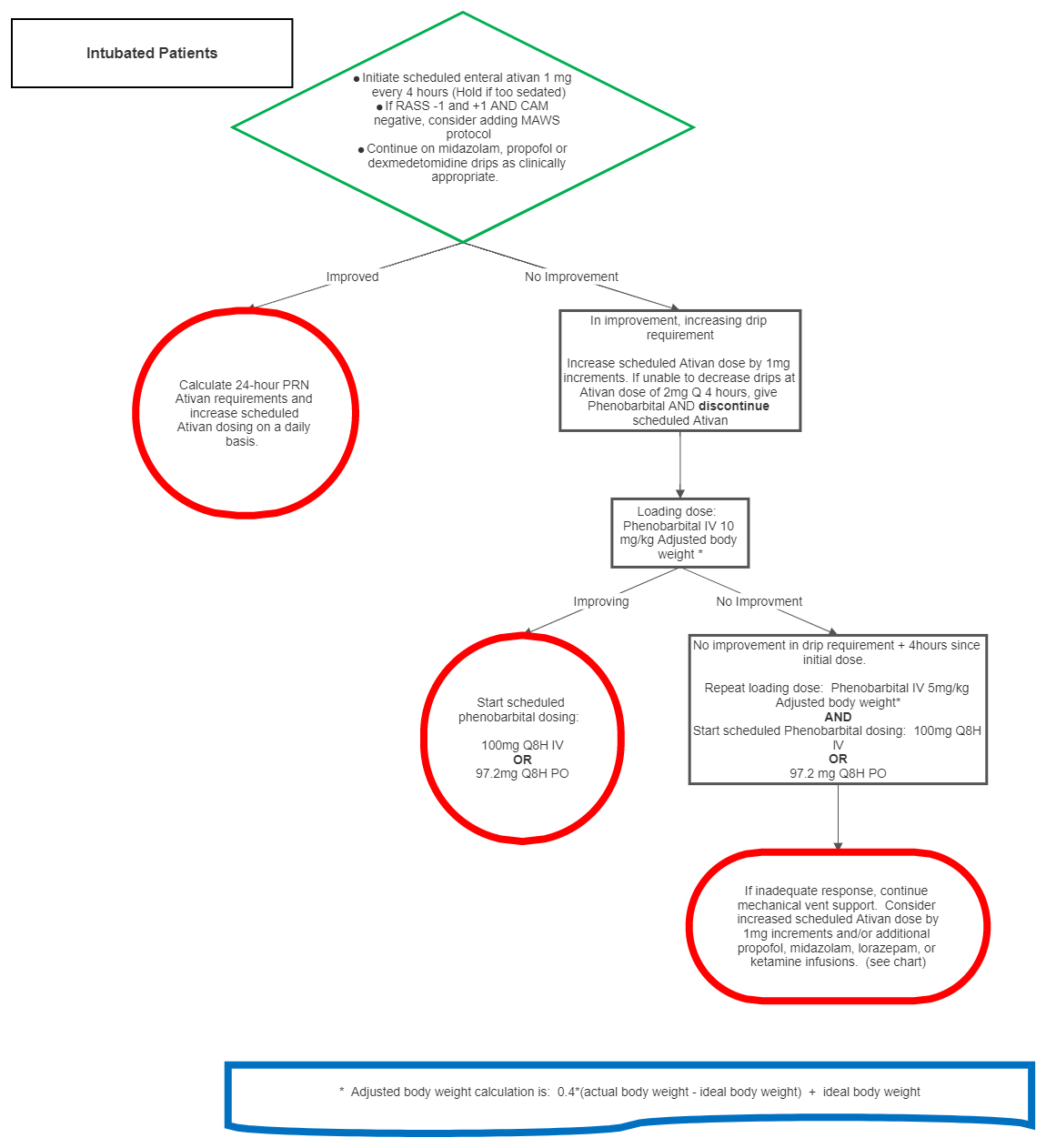
- Order multivitamin (PO), thiamine 100mg (PO or IV) daily, folate 1mg (PO or IV) daily for a minimum of 7 days
| Drug | Dose | Mechanism | Adverse effects | Monitoring | Tapering |
| Phenobarbital | See Algorithm | GABA Agonist |
|
Obtain ABG or VBG 2 hours after loading dose in non-intubated patients |
Reduce by 33% every 48 hours. Reduce dose first, and then dosing interval (ex. 100mg Q8H for 48 hours, 66 mg Q8H for 48 hours, 33 mg Q8H for 48 hours, discontinue) |
| Propofol | 5-80 mcg/kg/min IV |
GABA Agonist |
|
MUST be on mechanical ventilation Continue pulse ox |
|
| Ketamine | 0.15-0.3 mg/kg/hr IV | NMDA Antagonist |
|
Continue pulse ox |
|
| Dexmedetomidine (must use with concomitant benzodiazipine, barbituate or propofol) |
0.2-1.5 mcg/kg/hr IV |
Alpha 2 Agonist with sedative properties |
|
Continue pulse ox |
|
| Benzodiazepines | Varies based on agent. See above | GABA Agonist |
|
Continue pulse ox |
Reduce by 25% every 48 hours. Faster taper possible but must be discussed with interdisciplinary team. |