Burn: Adult Difficult to Resuscitate Protocol
exp date isn't null, but text field is
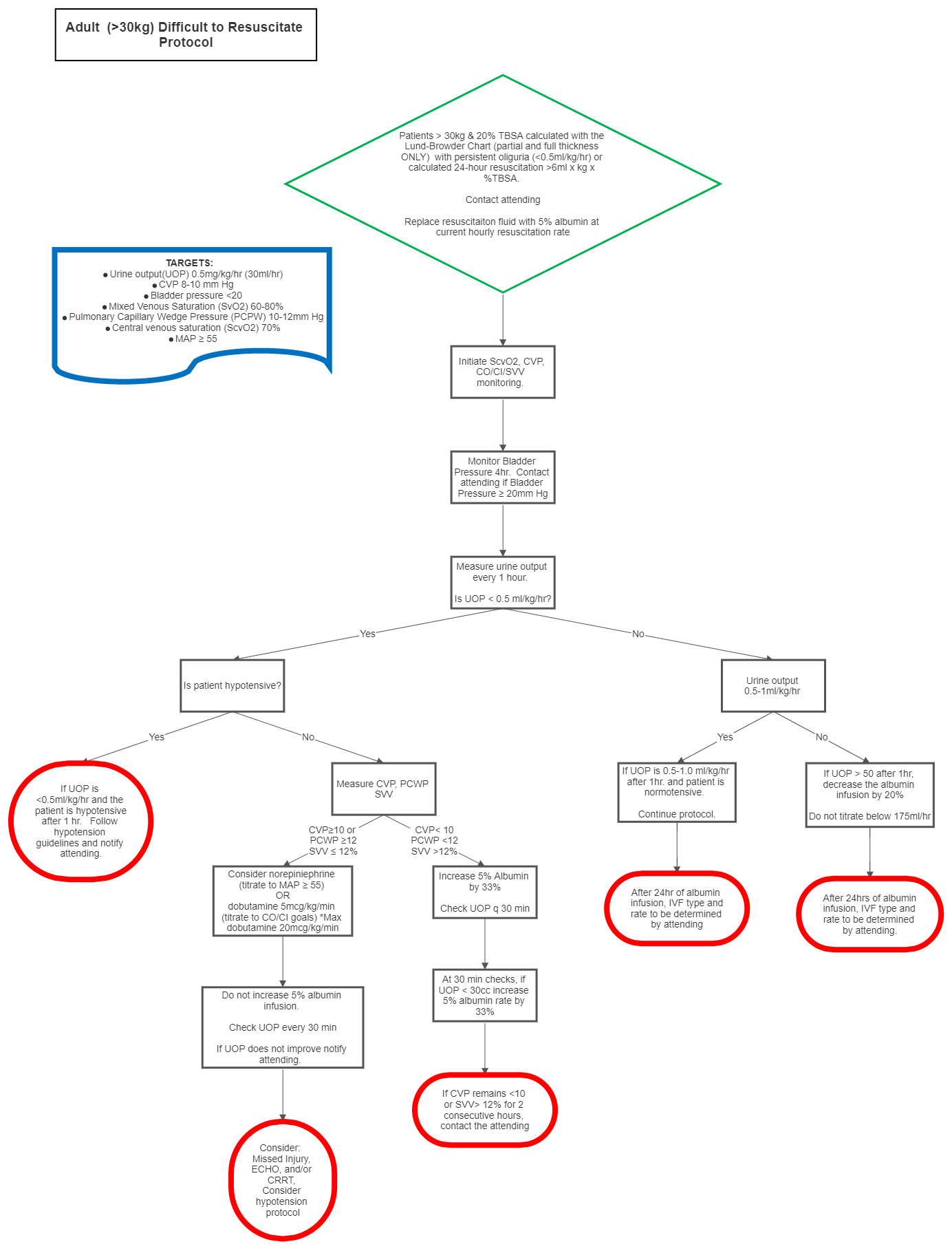
Switch from lactated ringers to 5% albumin. This is a standard concentration that comes pre-mixed from Pharmacy.
- Check bladder pressures every 4 hours.
- If urine output is less than 30ml/hr, strongly consider the placement of an invasive hemodynamic monitoring. Options include:
- The FloTrac sensor is a less invasive hemodynamic monitoring device that continuously measures and displays key flow parameters. With the Flotrac sensors, cardiac output, stroke volume, stroke volume variation, and SVR (derived from CVP) are available using a standard arterial pressure line and central line.
- The PreSep catheter is a triple lumen central venous oximetry catheter with an added capability for continuously monitoring central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2).
- Pulmonary artery (PA) catheter to guide resuscitation with specific pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) and mixed venous saturation (SvO2) goals.
- Esophageal Doppler Monitor (EDM)
- Titration of fluids should be guided by the Burn Attending with input from the following available parameters.
- If CVP or PCWP is not at goal then increase fluid rate by 33%
- If CVP or PCWP is at goal then consider levophed to augment mean arterial pressure (and thus UOP) or dobutamine 5mcg/kg/min (titrate until SvO2 or ScvO2 at goal.) Maximum dose of dobutamine is 20mcg/kg/min.
- If both CVP or PCWP and SvO2 or ScvO2 are at goal, then do not increase IVF rate any further (even if UOP<30ml/hr.) The patient should be considered hemodynamically optimized and the oliguria is likely a result of established renal insult. Some degree of renal failure is expected and should be tolerated. Continued increases in fluid administration despite optimal hemodynamic parameters will only result in “resuscitation morbidity,” that is oftentimes more detrimental than renal failure.
- Target Cardiac Output (CO) HRxSV/1000 = 4.0-8.0L/min
- Target Cardiac Index (CI) CO/BSA = 2.5-4.0L/min/m2
- Stroke Volume Variation (SVV) (SVmax – SVmin)/SVmean x 100 =10-15% (>13% consider additional volume, patient is dry)
- Target Mixed venous saturation (SvO2) 60-80%
- Target Central Venous Pressure (CVP) 10-12mmHg
- Target Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure (PCPW) 10-12mmHg
- Target Central venous saturations (Scvo2) 70%
- Target Mean Arterial Pressure ≥55mmHg
- Every attempt should be made in minimizing fluid administration while maintaining organ perfusion. If urine output is greater than 50ml/hr, decrease the fluid rate by 20%. Do not decrease the IVF rate below the calculated maintenance rate (175cc/hr).
If the patient switches to Difficult to Resuscitate and does not respond to colloid resuscitation, the resuscitation is no longer RN driven. Hourly monitor variables (e.g. CO, CI, SVV, ScvO2, CVP, urine output) will be communicated to the SBUR Attending and hourly fluid rate decided by the MD. These patients will be deemed Severely Difficult to Resuscitate and should be managed in close collaboration with the SBUR Attending and TBICU Critical Care Team.
Note: After 24 hours, infusion of LR should be titrated down to maintenance levels and albumin continued until the 48-hour mark at 0.5mL/kg/24hours 5% albumin.
DIFFICULT TO RESUSCITATE 5% ALBUMIN IN 0.45%NS
For difficult to resuscitate burn patient being changed from LR to albumin who meet at least one of the following criteria:
- Pediatric Patients
- >60% TBSA
- Pre-existing renal dysfunction
- Receiving NaCl resuscitation in the field or at the Outside Hospital