Hypotension in the Pediatric Burn Patient - Treatment Guideline
exp date isn't null, but text field is
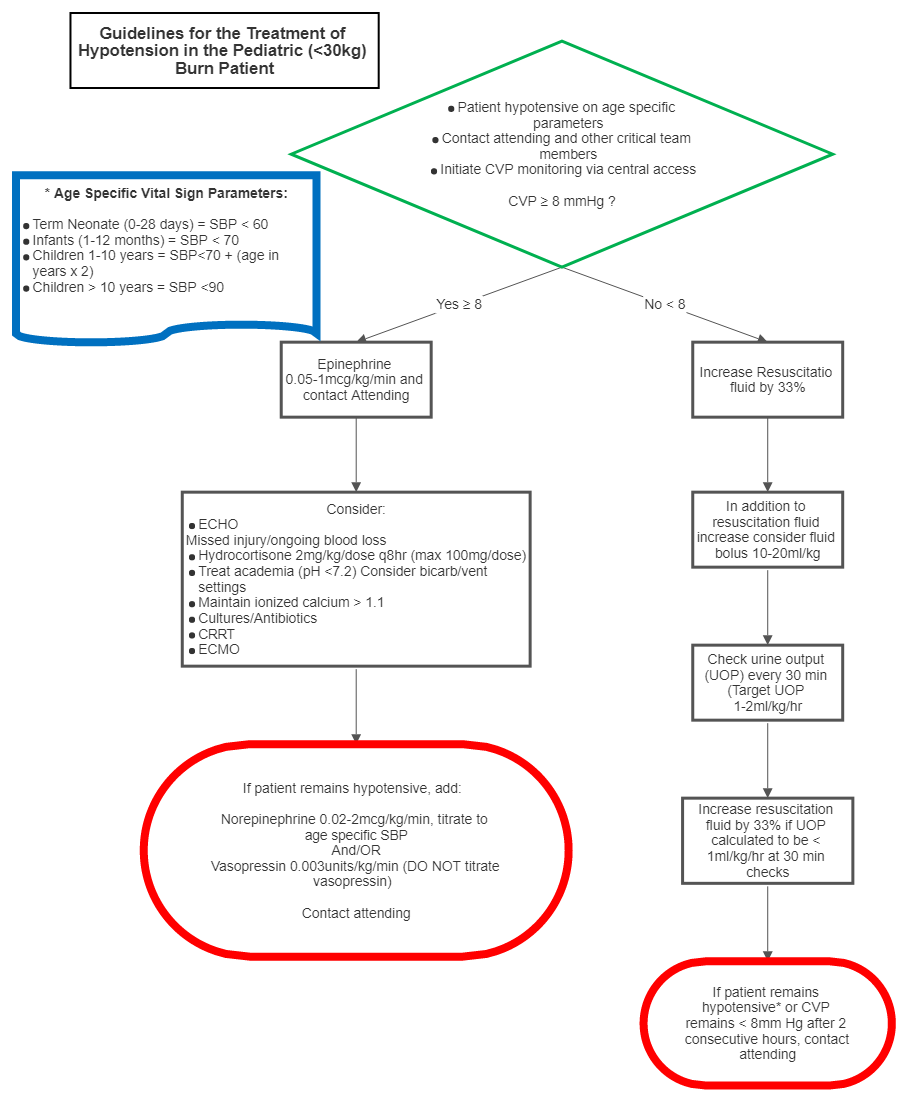
The optimal minimum blood pressure for burn patients must be individualized. Some patients will maintain adequate organ perfusion (and thus have adequate urine output) with mean arterial pressures (MAP) less than 70mmHg; therefore true hypotension must be correlated with urine output and overall perfusion. If a MAP (generally below < 55mmHg or below appropriate parameter for age) is not adequate to maintain the UOP target, the following steps are recommended:
- Monitor for hypotension
- Term Neonate (0-28 days) = SBP<60
- Infants (1-12 months) = SBP<70
- Children 1-10 years = SBP<70 + (age in years x 2)
- Children >10 years = SBP<90
- Contact Burn Attending AND Pediatric Surgery Critical Care Fellow
- Initiate CVP monitoring via central access
- If CVP ≥8
- Add epinephrine 0.05 – 1mcg/kg/min (titrate to age specific BP targets above) and call Burn Attending
- Consider
- ECHO
- Missed injury/ongoing blood loss
- Hydrocortisone 2mg/kg/dose Q8hours (max 100mg/dose)
- Treat academia (pH <7.2) – consider bicarb/vent settings
- Maintain ionized calcium >1.1
- Consider cultures/antibiotics
- CRRT
- ECMO
- Consider
- If persistent hypotension, add norepinephrine 0.05-2mcg/kg/min (titrate to age specific BP targets above) and/or vasopressin 0.003units/kg/min. DO NOT titrate
- Consider ECMO
- Add epinephrine 0.05 – 1mcg/kg/min (titrate to age specific BP targets above) and call Burn Attending
- If CVP <8
- Increase resuscitation fluid infusion by 33%.
- In addition, consider fluid bolus (10-20ml/kg)
- Check urine output Q30min (target 1-2ml/kg/hr)
- Increase IVF rate by 33% every 30 minutes until CVP >8, based on q30min urine output assessments
- If patient remains hypotensive or CVP remains <8 after two consecutive hours, contact burn attending
- Consider difficult to resuscitate protocol.
- Increase resuscitation fluid infusion by 33%.
- If CVP ≥8