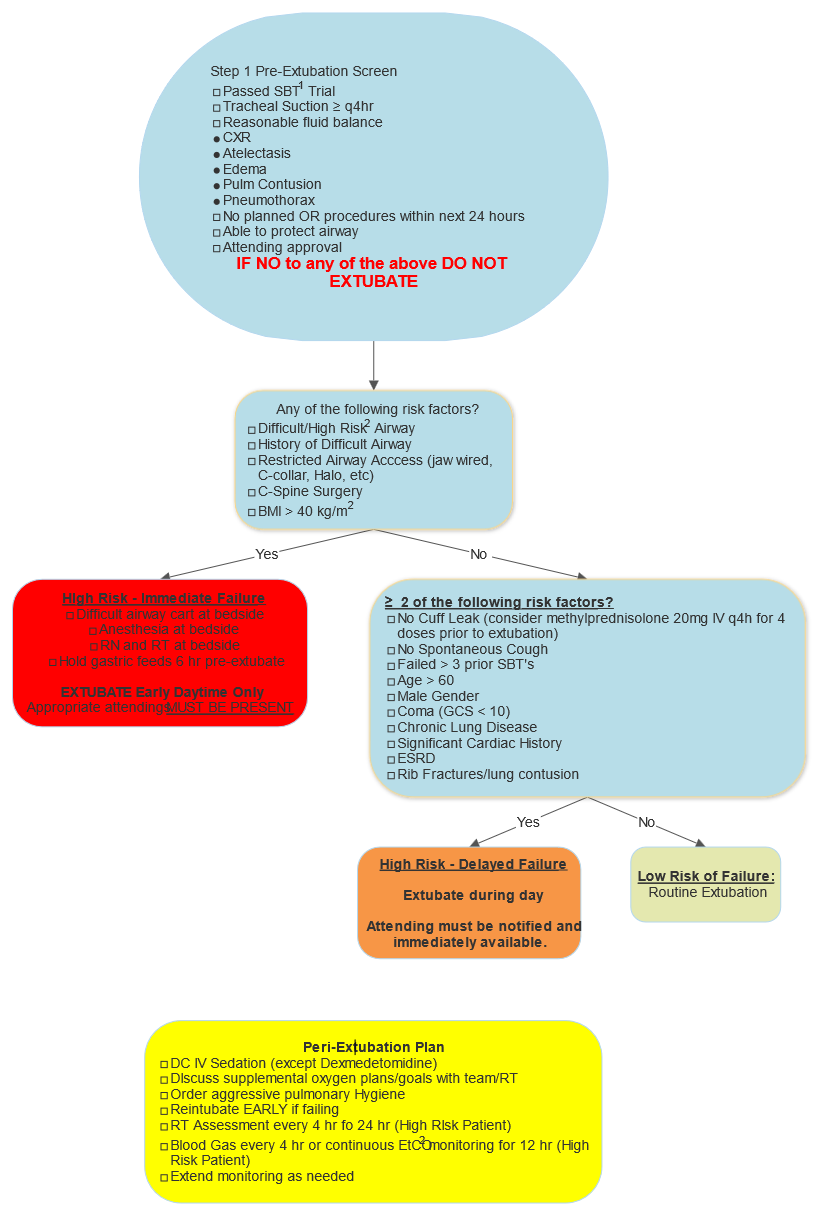
Extubation Evaluation/Checklist
exp date isn't null, but text field is
- Spontaneous Breathing Trial (SBT) Parameters: (To be routinely performed between 0800 and noon)
- Vent Settings Low (FIO2 ≤ 40%, PEEP ≤ 8)
- ABG adequate PaO2 and PaCO2
- Negative Inspiratory Force (NIF) < -30 cm H2O
- Tidal Volume (VT) > 5 cc/kg
- Vital Capacity (Vcap) > 10 ml/kg
- Respiratory Rate < 30
- Frequency Tidal Volume Index or Rapid Shallow Breathing Index (RSBI) < 104
- Difficult/High Risk Airway:
- Difficult or impossible face mask ventilation
- Difficult laryngoscopy
- Difficult or failed tracheal intubation
- Known/History of Difficult Airway
- Oral, pharyngeal, laryngeal, or tracheal abnormality (e.g. subglottic stenosis, tracheomalacia, peritonsillar deep space neck and retropharyngeal abscess, craniofacial abnormalities, Down's Syndrome, macroglossia, teratomas, lymphangiomas)
- Oral, pharyngeal, laryngeal, or tracheal surgery requiring special airway management (wired jaw)
- Limited neck movement (prior cervical fixation, immobilization, halo, cervical collar, or physically limited)
- Small mouth opening (less than 2 fingerbreadths)
- Inability to see uvula with the mouth open, tongue fully protruded
- Steven’s Johnsons Syndrome (SJS) or TENS
- Routine Extubation:
- Notify attending prior to extubation
- Perform extubation between 0800 and 1500, unless exempted by attending
- Heated High Flow (HHF) Recommendations
- Consider HHF in the following scenarios or any patients at high risk for reintubation:
- ≥ 65 years old
- Prolonged mechanical ventilation or difficult liberalization from mechanical ventilation
- BMI > 30
- Inadequate secretion management
- Patients with rib fractures
- Underlying chronic cardiac disease
- LV dysfunction
- LV EF ≤ 45%
- History of cardiogenic pulmonary edema
- Ischemic heart disease
- Permanent A-fib
- Underlying chronic lung disease
- COPD
- Obesity-hypoventilation syndrome
- Restrictive pulmonary disease
- Relative contraindication:
- Craniofacial/skull base fractures at risk for pneumocephalus (discuss whether heated high flow/positive pressure is safe with the trauma/face team)
- Consider HHF in the following scenarios or any patients at high risk for reintubation:
- Indicators a patient is failing extubation
- Respiratory distress
- Dyspnea
- Increased work of breathing (eg “belly breathing”)
- Increased or decreased respiratory rate
- Somnolence
- Hypercapnea (CO2 retention)
- Hypoxia
- Increased suction requirements
- Feeling of inability to breath or “impending doom”
- Inability to protect airway